
The ever-changing technology landscape is not a new revelation. And organizations are reimagining processes and strategies to accommodate it. With the birth of the digital age, cyber-attacks are on the rise. Various studies show that small and mid-size businesses (SMBs) are more prone to cyber threats, and having solid defenses to protect your business has become more challenging. The problem worsens when traditional security solutions fail to stop these advanced attacks.
Large enterprises can recover from data breaches, but small businesses take weeks or months to discover it. A Cisco research report reveals that 74% of SMBs in India suffered a loss in revenue due to cybersecurity incidents. But, Indian firms bank on advanced technologies to accelerate their business reach and cannot afford to back out due to persistent cyberattacks. Right now, businesses of all sizes must proactively engage in securing sensitive data and engage in preventing cyber threats.
Importance of IT in enabling SMBs
Cloud Computing
Cloud services are more feasible than traditional infrastructure storage. The benefits of using the cloud are not just limited to revenue growth, but it is an enabler of growing partnerships and strategic marketing of products and services. Along with the prominent offers of cloud technology, such as flexibility and adaptability, it offers scalability and lower maintenance required by SMBs. For example, Pansari Group, which deals with food items, digitized its operation channels and used cloud storage to supervise production cost-effectively.

Analytics
Data analytics is critical for SMBs’ growth; implementing it can increase revenue, efficiency, and productivity. A data-centric approach will utilize the high amount of data generated from the business to complete the customer journey picture. Data as a Service (DaaS) is gaining popularity among companies as they offer data storage, collection, and analysis. Data analytic tools offer SMBs to drive more traffic to their websites, push customers through the conversion funnel, and help understand market conditions and forecast emerging trends.
eCommerce operations
Service-based SMBs pivoted their business online and expanded their revenue by jumping into the digital sales channels’ bandwagon. eCommerce technology is doing wonders by benefitting the business reach at a low operational cost. It is helping SMBs with omnichannel distribution networks and virtual alternatives by replacing “in-person” meetings and providing virtual services. For example, Amazon has launched the “Spotlight Northeast” storefront to leverage the benefits of eCommerce to SMBs.

Digital Payments
Payment technology is unlocking significant value for SMBs. It eliminates the manual process of managing cash flow and recording payroll and disbursement of transfers to customers. Digital payments address conventional payment processes by introducing digital wallets, NFC payments, and online payments. It has significantly reduced the administrative burden by improving customer experience, reducing costs, and cloud-hosting the transactions.
Digital solutions have remarkably reduced the woes faced by SMBs. It has helped them expand and accelerate their digital footprints and is playing a more significant role in their business processes. But at the same time, tech adoption has exposed SMBs to cyber threats and attacks. To help SMBs realize the benefits of digital solutions while preventing cyber risks, let us dig deeper into learning how to monitor and analyze all resources and keep them secure effectively.
What are the cybersecurity threats for Small Businesses?
A cyber threat is when a malicious actor attempts to disrupt or damage your digital data and assets and potentially cause harm to your network system.
Phishing Attacks
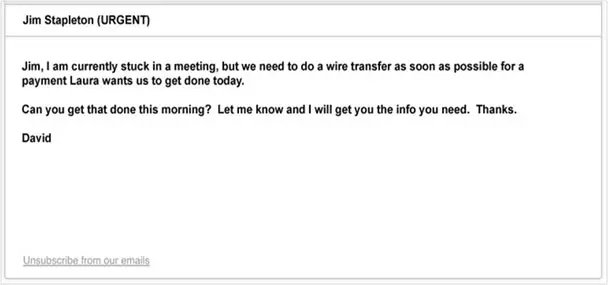
The small business mainly faces this kind of attack called phishing attack. Here the attack is executed by manipulating users to click on unsuspicious links or design fake web pages to collect sensitive information. For example, an organization we partnered with shared an experience of how a spoof email for payment was sent to the client where the scammer forged the email address.
Although there is widespread awareness of how phishing attacks occur, thanks to the notoriety of hackers, it is easy to get swayed by it.
Spear phishing:
Spear phishing involves email; here, the attacker already has basic information about the victim, such as the name, job title, and email address. The attacker puts urgent explanation leaving no time for the victim to think about it. Spear phishing also lures people to download malicious software or codes which allow them to access sensitive information.

Whaling attack
In a whaling attack, the attacker aims at senior executives in an organization. Here the sent email is more sophisticated and conveys the message with a solid business tone. The emails might not be crafted with heavy technical knowledge, but it is enough information to trap senior officials in initiating the funds transfer. These attacks are usually done through cloud storage, eCommerce platforms, and file hosting sites.
Malware Attacks
Malicious software is otherwise known as malware. It is an umbrella term for various intrusive software such as computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, and ransomware. There is always a sentiment that small business owners think they are small compared to large enterprises to get attacked by cybercriminals. These allow malware designers to create false identities and go after SMBs to extort money and data and violate customer information. There is another reason for hackers to attack small businesses. As SMBs tend to allow employees to use their personal devices for work, this gives them more reason to infect devices and gain access to the network quickly.
Weak Passwords
It’s a headache to remember passwords for different accounts, plus it gets confusing. Putting weak or compromised passwords on confidential information is like giving keys to cyber attackers. A survey reported that an average of 19% of professionals put easy-to-guess passwords or share them in different accounts. Due to a lack of awareness, small business often tends to go easy on keeping a strong password to protect systems. Attacker bots use compromised credentials to get into other account details. This is called credential stuffing. 65% of users reuse their passwords to log in to other accounts, according to a Google survey.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a cybercrime where the attackers hijack a computer system by sending fake requests to the target host’s server. This forces websites to go down, making the websites unavailable for everyone. As SMBs have lax security practices, they might not spot a DDoS attack in the first attempt as the websites slow down or goes offline.
Why are SMBs target of cyber attacks
Many reports, surveys, and statistics assert that hackers focus more on small businesses due to the absence of proper security precautions and measures. Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach reported that cyber threat attackers attacked 43% of SMBs. An IBM security study showed that 40% of small businesses said that during the pandemic, they were targeted more with malicious spam emails.
SMBs are easy prey:
Small businesses have assumed a false sense of security due to small-scale operations. Often cybersecurity doesn’t show up as the top business priority due to perceived cost. This makes them more prone to malicious attacks and data exfiltration.SMBs can be the stepping stone for a larger enterprise:
Due to the robust security defences in place by large organizations, cyber attackers find their way out. As small businesses are a part of a larger supply chain, attackers find a way to breach the larger organizations.
The attackers go “one small step at a time” and find the loopholes to enter a bigger enterprise, which results in finance and reputational damage for the small businesses.SMBs are vulnerable to personal details:
Cybercriminals target SMBs as they are aware that they lack technical details or know-how for cyber security measures. For example, with the help of phishing emails, they attempt to take out personal information, hack into system networks, and cripple devices.
Also, small businesses are coerced into paying ransom money to hackers to recover personal and sensitive information like bank details, health records, and social security data. Following are some of the basic guardrails SMBs must have in place to ward off threats.
Cybersecurity best practices for SMBs
To combat cyber threats, SMBs must pivot to taking proactive measures before an actual cyber attack takes place. Cyber security doesn’t require spending a tremendous amount of money or hiring an in-house IT staff. Here are some of the best practices that will protect employees, networks, and systems to stay or prevent a possible breach and data loss in the future.
Security goes beyond antivirus software:
Cyberattacks have the potential to come from anywhere, navigating around antivirus software and firewalls. Many small businesses consider antivirus software protection enough to dodge cyber threats. Insider threats from compromised employee accounts aren’t protected by antivirus software.
Advanced threat actors can work beyond signature-based security tools and hack into business accounts. Antivirus doesn’t cover advanced persistent threat (APT)- a typical malware attack that infilters internal data and network to collect information.Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA):
Multi-factor authentication, also called two-factor authentication, acts as an additional protective security layer to authenticate users. Using MFA, SMBs can ensure suspected log-ins and set alerts in real-time.
MFA also leverages efficiency and is considered a “relatively low-effort step” for SMBs as they can easily attain security benefits. It also minimizes the effort to create new passwords or type in existing ones.Training employees:
Cybersecurity training programs help underprepared employees and help them to have a basic framework in place. A quarterly or biannual training program to address safety policies like going through policy updates, and flagging non-work-related emails and suspicious links from unknown sources will reinforce the importance of security.Protect important files:
Regularly back up important files on cloud and external hardware devices. This step is one of the underrated but essential measure to prevent a ransomware attack. Creating a strategic backup will be a much-needed relief to regain control over the system.Zero-trust approach:
SMBs can effectively incorporate a zero-trust model by using “Never trust, always verify” into practice. As remote and hybrid employees have access to the company’s network, a zero-trust approach will enable all end-points to act as an added layer of protection.
How can Neekan help you?
With decades of experience in the IT domain, we know what it takes to secure digital assets from different types of threats. Our deep expertise on the security standards, compliance requirements helps us offer comprehensive, end-to-end solutions that will not only help you recover from any attacks but also safeguard from any attacks in the future.
Reach out to us to discuss your IT infrastructure problems and needs with our experts

